AERIAL MAPPING SURVERY PHOTOGRAPHY
AERIAL SURVEY
Aerial Survey is a form of collection of geographical information using airborne vehicles. The collection of information can be made using different technologies such as aerial photography, radar, laser or from remote sensing imagery using other bands of the electromagnetic spectrum, such as infrared, gamma, or ultraviolet[1]. For the information collected to be useful this information needs to be georeferenced. The georeferencing of information is usually done using GNSS with similar techniques as the techniques used for dynamic land surveying.
Application Architecture
Aerial Surveying is normally done using manned aeroplanes where the sensors (cameras, radars, lasers, detectors, etc) and the GNSS receiver are setup and are calibrated for the adequate georeferencing of the collected data. Apart from manned aeroplanes, other aerial vehicles can be also used such as UAVs, balloons, helicopters.
Usually for this type of applications, kinematic methods are used. The algorithms used in these dynamic surveys rely on the fact that while the receiver move through the air should never loose lock on the satellites signal. The techniques and algorithms used can be used in post-processing since usually the positioning data is not required in real-time.
Multiple sensors of different or similar types can be used in order to collect different types of information or to be able to build 3D computer models of the terrain (e.g. stereoscopic cameras).
The data collected can be used for different purposes such as:
- Sea surveys (sea level, temperature, undulation, etc)
- Land survey (cartography, topography, feature recognition, etc)
- Monitoring vegetation and ground cover
- Reconnaissance
Application Characterization
The 3D visualization of the data collected by aerial surveys can be created by georeferencing the aerial photos and other sensor data (laser, radar,...) in the same reference frame, orthorectifying the aerial photos, and then draping the orthorectified images on top of the other sensors grid. It is also possible to create digital terrain models and thus 3D visualisations using multiple aerial photographs. Techniques such as adaptive least squares stereo matching are then used to produce a dense array of correspondences which are transformed through a camera model to produce a dense array of x, y, z data which can be used to produce digital terrain model and orthoimage products.
Application Examples
Two of the most used forms of Aerial Survey are:
- Aerial Laser Profiling - Aerial Laser Profiling uses short duration laser pulses that are emitted towards the ground, reflected and detected by a receiver in the airborne vehicle. The time between the emission of the pulse and the reception can be used to determined the distance travelled by the pulse.
- Aerial Photogrammetry - In aerial photogrammetry aerial photos are taken in order to produce 2D or 3D terrain models. Multiple cameras might need to be used to build 3D models

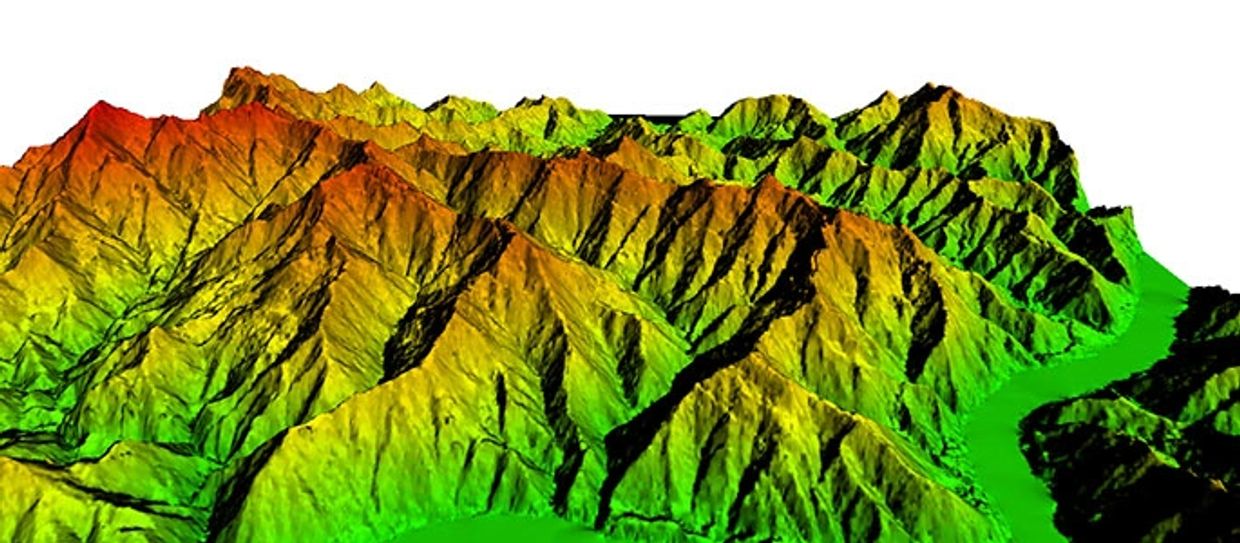
Aerial Imagery & Aerial Photogrammetry
Aerial imagery provides a record of the earth's surface at an instant in time and is relied on by all organisations that manage or interact with the natural and built environments. Aerial imagery provides a common language to help communicate complex concepts or problems to developers, planners, decision makers and society at large.
Aerial photogrammetry is a method of surveying involving the measurement and interpretation of features directly from aerial photographs. Aerial photogrammetry complements aerial imagery and airborne LiDAR derived datasets.

Some applications of aerial imagery include:
Governments use aerial imagery to help monitor and manage environmental change
- Local governments use aerial imagery to improve town planning
- Mining companies use aerial imagery to help quantify and manage disturbance and rehabilitation
- Engineers rely on aerial imagery to help determine optimal route location and design for major infrastructure projects
- Emergency services rely on rapid-response aerial imagery to help assess damage caused by natural disasters and plan future mitigation strategies.

Some applications of aerial photogrammetry include:
Topographic mapping
- Precise mapping of building outlines and roof structures to create 3-dimensional city models
- Volumetric determination of stockpiles and mine voids
- Preparation of Land Use maps
High resolution digital aerial cameras coupled to airborne LiDAR systems allow imagery to be captured with LiDAR simultaneously, minimising project costs.
Several of AAM's digital aerial cameras allow the infrared spectrum to be captured in addition to conventional visible light, benefiting applications for environmental, agricultural and forestry purposes.
High spatial resolution and good quality of images display the real situation on the surface. With the aerial survey we are able to get high-res images even of those territories that are covered with dense vegetation.
There are several types of aerial survey:
- Colour aerial survey repeat natural colours of a landscape. This makes the images more informative and realistic;
- Thermal aerial survey helps to analyze an object remotely. This method is used for urban infrastructure monitoring (pipes, water supply system, sewage, etc.), centers of ignition detecting, livestock tracking and so on.
- Digital infrared aerial survey is used for creating images in synthetic ("not natural") colours. All changes on the surface are displayed in different shades.
As a result a customer gets relevant and reliable image of the surface. Basing on these
- image one can create following products:
- topographic maps and plans;
- GIS projects;
- digital elevation models;
- longitudinal and transverse terrain profiles;
- virtual tors;
- 3D panorama;
- geospatial database.
Aerial survey is widely used by:
- real estate developers, investors, building contruction companies;
- marketing, advertising companies;
- geological and mining companies, archeological organizations;
- agricultural companies;
- web-portals;
- film production companies.